Elon Musk Confirms First Successful Human Neuralink Implant
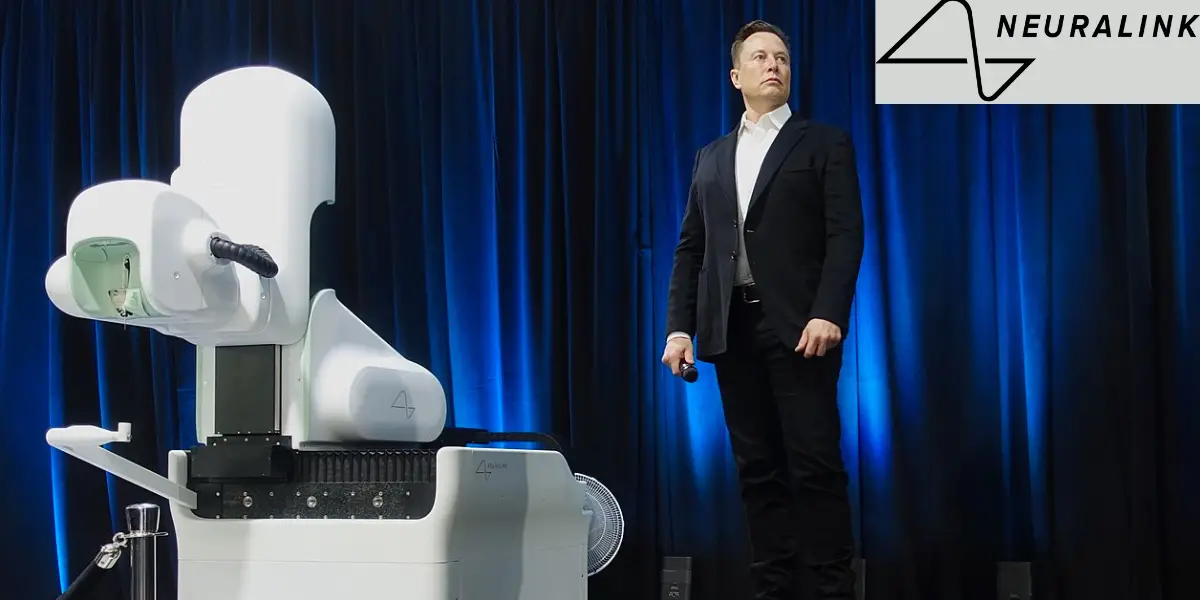
In the rapidly evolving field of neurotechnology, Neuralink stands out as a pioneering venture co-founded by visionary entrepreneur Elon Musk. This ambitious project aims to develop high-bandwidth brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) to enhance human cognitive capabilities, treat neurological disorders, and facilitate a symbiotic relationship between humans and artificial intelligence. With its groundbreaking first human brain implant successfully completed, Neuralink has catapulted into the spotlight, promising a future where the boundaries between the human mind and machines blur.
Neuralink, Elon Musk’s neurotechnology venture, has achieved a milestone with its first successful human brain implant.
Table of Contents
First Human Neuralink Brain Implant Successfully Completed
In a groundbreaking development, the first human Neuralink brain implant was successfully completed, as announced by Elon Musk on January 29, 2024. This historic event marks a significant milestone in the field of neurotechnology, showcasing the potential of brain-computer interfaces to enhance human capabilities and treat neurological disorders. The successful implantation demonstrates Neuralink’s advanced technology’s safety and efficacy, paving the way for future applications in medical treatment and human-AI integration. This achievement not only highlights the technical prowess of Neuralink but also opens up new possibilities for the future of human cognition and health.

What is Neuralink?
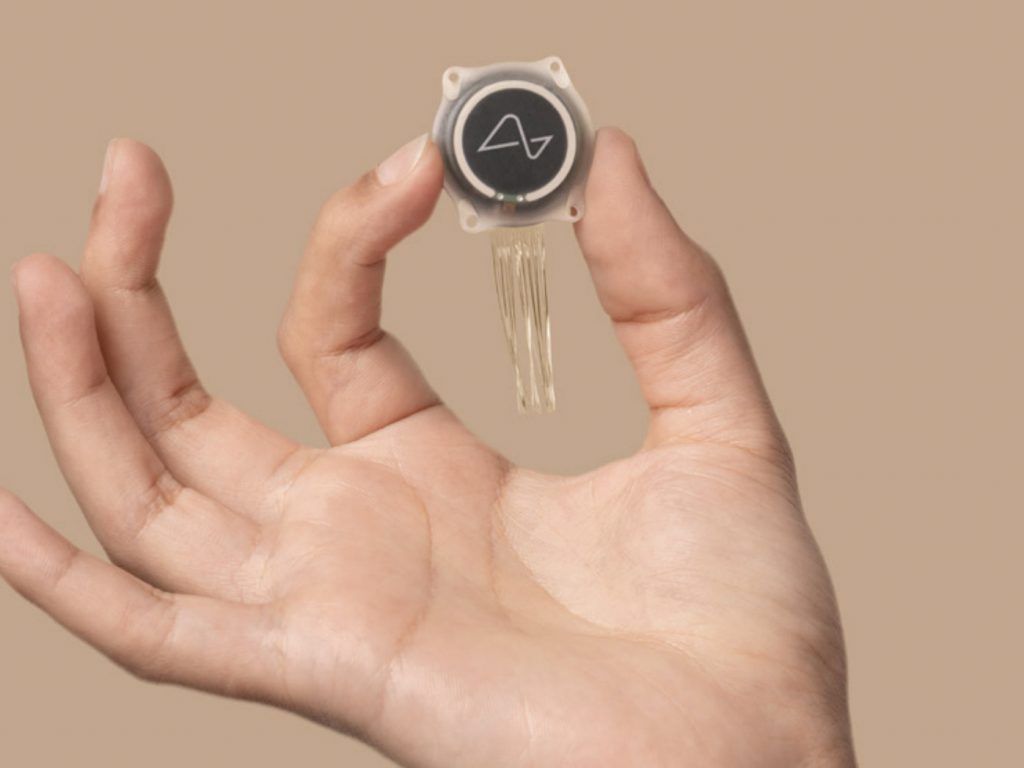
Neuralink is a neurotechnology company co-founded by Elon Musk, aimed at developing advanced brain-computer interfaces (BCIs). Established in 2016, the company’s mission is to enable direct communication between the human brain and computers, potentially revolutionizing how we interact with technology and treat neurological disorders. Neuralink’s technology involves ultra-thin, flexible electrode threads that can be implanted into the brain to monitor neural activity and stimulate brain regions, offering both medical applications and the enhancement of cognitive abilities.
The company’s vision extends beyond medical treatment, aspiring to facilitate a symbiotic relationship between humans and artificial intelligence. This ambitious goal seeks to augment human intellect, potentially allowing for direct thought-to-digital communication, enhanced sensory perception, and improved cognitive functions. Neuralink’s advancements in BCI technology hold the promise of significant breakthroughs in understanding and interfacing with the human brain, offering a glimpse into a future where the boundaries between the biological and digital worlds blur.
Who is Elon Musk?
Elon Musk is a visionary entrepreneur and business magnate known for his role in founding and leading several high-profile technology companies. Born on June 28, 1971, in Pretoria, South Africa, Musk has become a pivotal figure in advancing renewable energy with Tesla, Inc., revolutionizing space travel with SpaceX, and exploring high-speed transportation with the Hyperloop concept. Musk’s ventures into neurotechnology with Neuralink aim to merge human cognition with artificial intelligence, further showcasing his commitment to addressing global challenges and pushing the boundaries of technological innovation. His work has not only transformed industries but also sparked widespread discussions on the future of humanity, space colonization, and the ethical implications of AI.
Also read:What’s the Relationship between Quantum AI and Elon Musk?,Why does Elon Musk Make Twitter Rebrand?

The Role of Neuralink
Neuralink, Elon Musk’s ambitious venture into neurotechnology, aims to bridge the gap between humans and rapidly advancing artificial intelligence.
Enhancing Human Capabilities
- Direct Brain-to-Computer Communication: Enables real-time, high-speed information transfer between the human brain and computers.
- Augmented Cognitive Abilities: Could enhance memory, learning speed, and thought processing.
- Enhanced Sensory Inputs: Potential to add new sensory inputs or augment existing ones, such as vision or hearing.
Medical Applications
- Treating Neurological Disorders: Potential applications in treating conditions like Parkinson’s disease, epilepsy, and depression.
- Brain Injury Rehabilitation: Could aid in the recovery of brain function following strokes or traumatic injuries.
- Prosthetic Control: Enhances the control and feedback of prosthetic limbs for amputees, restoring a sense of touch and movement.
Bridging Humans and AI
- Symbiosis with AI: Aims to create a future where humans can seamlessly integrate with AI, enhancing decision-making and creativity.
- Preventing AI Dominance: By augmenting human intelligence, Neuralink hopes to prevent a future where AI surpasses human capabilities and becomes uncontrollable.
- Enhanced Communication: Could lead to new forms of communication between humans and AI, as well as between individuals, transcending language barriers.
How Does Neuralink Affect the Brain?
Step 1: Ultra-thin electrode threads are surgically implanted into the brain, targeting specific areas to monitor and stimulate neural activity.
Step 2: These electrodes detect electrical signals produced by neurons, enabling the recording of brain activity in real-time.
Step 3: The recorded signals are transmitted to an external device, where they are analyzed and interpreted by sophisticated algorithms.
Step 4: Based on the analysis, the system can send signals back to the brain, influencing neural activity and potentially restoring or enhancing cognitive functions.
Step 5: Over time, the system learns from the brain’s responses, optimizing its stimulation patterns to achieve desired outcomes, such as improved motor control or cognitive abilities.
Step 6: The interface facilitates a two-way communication channel between the brain and external devices, potentially allowing for direct brain control of computers, prosthetics, and other technologies.

Neuralink Animal Testing
Neuralink’s journey through animal testing has been marked by significant milestones and controversies, as outlined below:
- 2017-2020: In partnership with UC Davis, Neuralink conducted experiments on monkeys, aiming to refine their brain-computer interface technology.
- April 2021: Demonstrated a monkey playing the game “Pong” using a Neuralink implant, showcasing the device’s potential to interpret neural signals into actionable commands.
- 2022: Allegations arose from the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine (PCRM) claiming mistreatment of monkeys, leading to psychological distress and chronic infections from surgeries.
- February 2022: Neuralink acknowledged the death and euthanization of macaque monkeys post-experimentation, denying any form of animal abuse.
- December 2022: Reports emerged of a federal investigation by the USDA into Neuralink’s animal welfare practices, spurred by internal concerns over rushed testing leading to animal suffering.
Neuralink Human Testing
Neuralink’s progression to human testing represents a critical step towards realizing its ambitious goals, with key events including:
- May 2023: Received FDA approval for human clinical trials, overcoming previous rejections due to safety concerns related to the device’s components and implantation process.
- September 2023: Began recruitment for its first human trials under an investigational device exemption granted by the FDA.
- January 29, 2024: Elon Musk announced the successful implantation of a Neuralink device in a human subject, marking a historic milestone in the company’s development and opening new possibilities for the application of its technology in medical and cognitive enhancement fields.
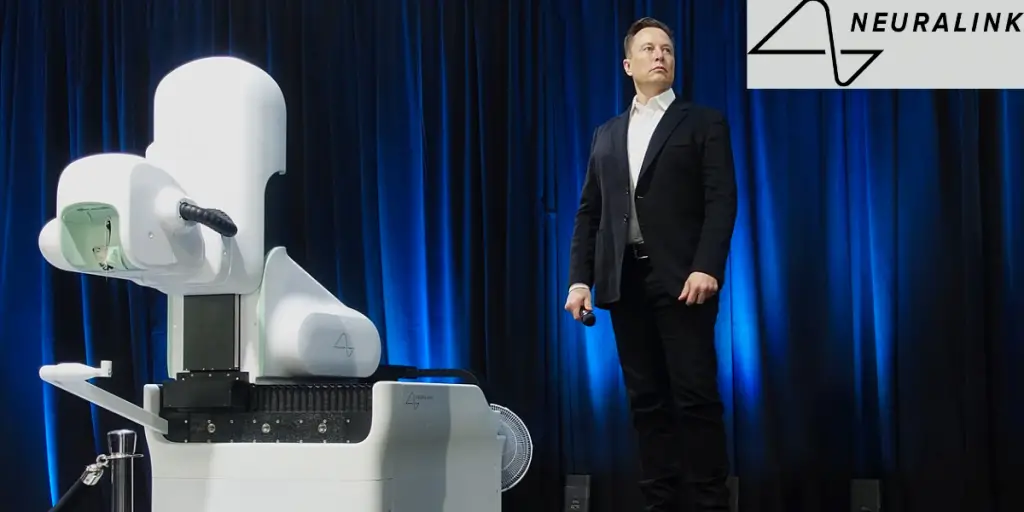
How Did Neuralink Get FDA Approval?
Addressing Safety Concerns
Neuralink’s path to FDA approval involved rigorous testing and refinement to address initial safety concerns. The FDA’s scrutiny focused on the biocompatibility of implant materials, the potential for long-term neural damage, and the reliability of the device under various physiological conditions. Neuralink demonstrated through extensive preclinical studies that their device could be safely implanted and operated within the brain, with minimal risk of infection, rejection, or significant tissue damage.
Technological Innovations
A key factor in gaining FDA approval was Neuralink’s innovative approach to brain-computer interface technology. The company developed ultra-thin, flexible electrode threads that reduce the risk of brain tissue damage compared to traditional neural implants. Additionally, Neuralink’s robotic surgical procedure for implantation, designed to be precise and minimally invasive, further convinced the FDA of the procedure’s safety and efficacy.
Clinical Trial Design
Neuralink’s proposal for a well-structured clinical trial played a crucial role in securing FDA approval. The company outlined a clear, phased approach to human testing, beginning with a small group of participants to closely monitor the device’s performance and patient safety. This cautious and methodical approach reassured the FDA that Neuralink was committed to patient safety and the scientific integrity of their trials.
Neuralink Has Been Controversial
Ethical Concerns
Neuralink’s work has sparked ethical debates around the implications of merging human brains with computers. Critics question the long-term societal impacts, including issues of privacy, autonomy, and the potential for exacerbating social inequalities. The prospect of enhancing human capabilities also raises concerns about the definition of normal human experience and the potential for creating a divide between those with and without enhancements.
Animal Welfare
Animal testing conducted by Neuralink has been a significant source of controversy. Allegations of mistreatment and the euthanization of test subjects have drawn criticism from animal rights groups and raised questions about the ethical standards of Neuralink’s preclinical research. These concerns have led to federal investigations and public backlash, challenging the company’s ethical practices.
Regulatory and Safety Concerns
Neuralink’s ambitious goals and rapid development pace have raised concerns about the adequacy of current regulatory frameworks to ensure the safety and efficacy of such advanced neurotechnology. Critics argue that the long-term effects of brain implants are still largely unknown, and the rush to bring such devices to market may overlook potential risks and ethical dilemmas associated with brain-computer interfaces.
Conclusion
Neuralink represents a significant leap forward in the realm of neurotechnology, with its successful human implant marking a pivotal moment in the integration of humans and advanced computing. While the technology holds immense potential for medical breakthroughs and cognitive enhancement, it also raises critical ethical and safety concerns that society must address. The journey of Neuralink, from animal testing to FDA approval and the controversies it has sparked, underscores the complex interplay between innovation, ethics, and regulation. As we stand on the brink of this new frontier, the continued development of Neuralink will undoubtedly shape the trajectory of human evolution and our relationship with technology.

